As you know, we have already covered the basic concept of complexity and Big-O. So, now it’s time to learn that how we can calculate or find the complex nature of any given code.
Before moving on let me tell some rules that we need to apply so that we can calculate the complexity quickly.
- Any statement that has addition, subtraction, assignment statement, if, if-else, update variable value or memory access, takes one step to get execute
- Loop or subroutine fraction takes N time.
Where N is the number of time for which loop will execute
For example for(i=1; i<=n; i++) and suppose n=10; for(i=1; i<=10; i++)
- Drop all insignificant constants or constant multiplier.
Reason:
Suppose we have MN + C and let M=2 and C=10
then we can write 2N + 10;
We always care about the running time when N becomes larger or infinite. So, If we consider N is one million, then the first part 2N will become 2 million and the second part (+10) will remain constant and don’t have any effect. So, that’s why we drop all the constant. 2N is not a unit to define the proper execution time complexity if we have a different machine with different processor and memory, i.e., core i7 or super computer and if we apply the rule, we got N.
Finally, O( N) will be the complexity of we have 2N + C;
Also, if we have n3 + n, then as we know, if n becomes larger than +n become very insignificant. So, complexity will be O(n3).
Let’s try some examples
Example # 1:

Example # 2:
Loop inside another loop (Quadratic example )

Example # 3:
If or if-else inside the loop (linear example)

Example # 4:
Cubic big o loop example

Example # 5:
Linear Big – O example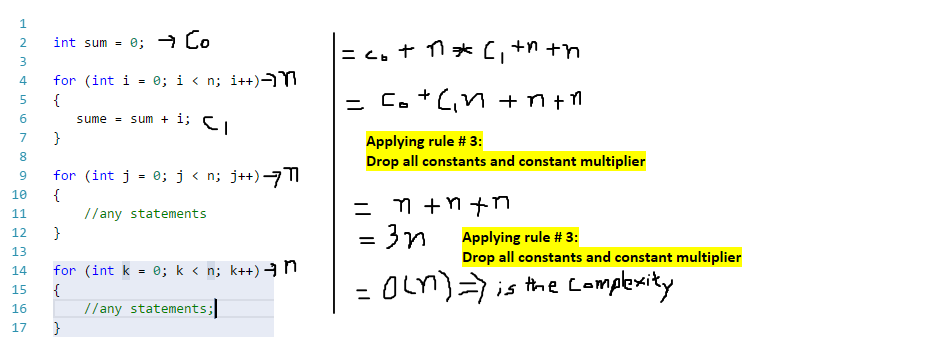
Example # 6:
Logarithmic example
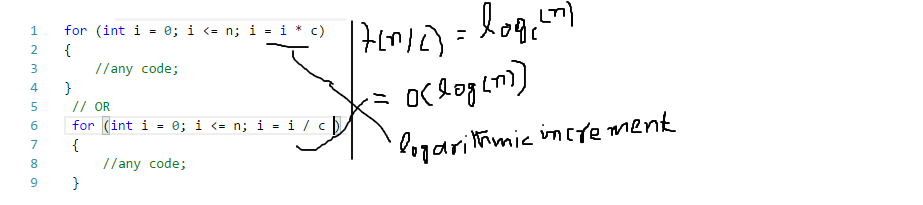
I think above examples are enough. If you have not read about what is complexity or Big-O, then I strongly recommend you to read this blog post (Code complexity and Big-O notation)
Big – O notation summary
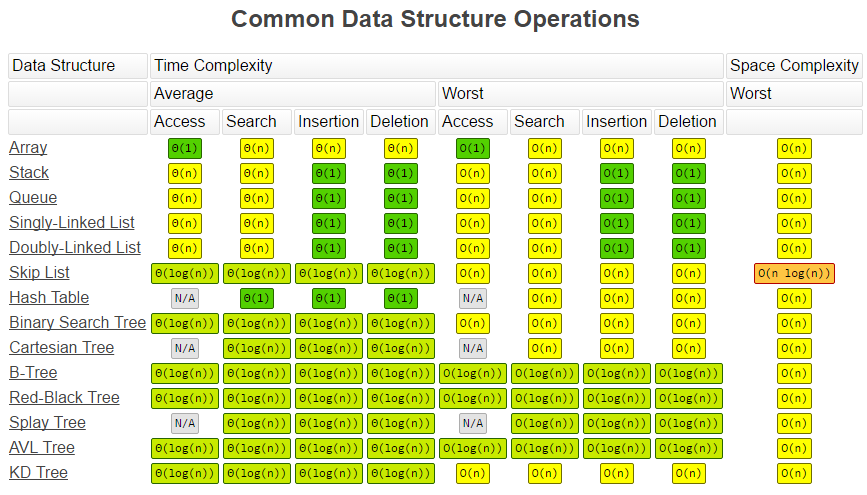
And
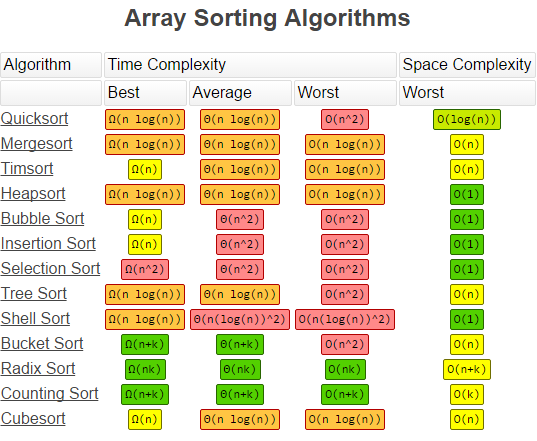
If you need any help or want to give any suggestion, you are welcome I will appreciate you.